what phase is cytokinesis completed Cytokinesis: definition, steps, and significance
Have you ever heard of the term “cell cycle regulation?” It’s a fascinating topic that is connected to the essential process of cell division. Within the larger umbrella of cell cycle regulation, there are two key players: cyclins and CDKs. Without these two, cells wouldn’t be able to properly develop and maintain themselves. Cyclins are proteins that assist in regulating the cell cycle by binding to cyclin-dependent kinases, or CDKs. CDKs, in turn, are enzymes that help in the regulation of cell division by phasing the cycle from one stage to the next via the addition or removal of various molecules. Why are these two players so important? Without proper regulation, cell division can go awry and result in issues such as cancerous growths. Cyclins and CDKs act as checkpoints, ensuring that each stage of the cell cycle is completed accurately before progressing to the next. To better understand this concept, let’s dive deeper into mitosis, the process by which one cell divides into two daughter cells. During mitosis, there are five distinct phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase: Chromosomes condense, and the nuclear membrane breaks down. The spindle fibers begin to form. Prometaphase: The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes, and the microtubules move them to the center of the cell. Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell, known as the metaphase plate, which ensures that each daughter cell receives an accurate copy of the genetic material. Anaphase: The spindle fibers pull the duplicated chromosomes apart, separating them into individual chromatids that are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. Telophase: The chromosomes begin to unwind and revert to their uncondensed state, and the nuclear membrane begins to form around each cluster of chromosomes. Each of these phases is carefully regulated by cyclins and CDKs, ensuring that the division is completed accurately and efficiently. Without these proteins, the cell cycle could become uncontrolled, leading to issues such as developmental defects or the formation of tumors. It’s truly incredible how much goes into the seemingly simple process of cell division. Next time you think about how our bodies are made up of trillions of cells, remember the crucial role of cyclins and CDKs in their development and regulation. Images:
Mitosis Illustration
 This illustration depicts the stages of mitosis, from prophase to telophase, and how chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells.
This illustration depicts the stages of mitosis, from prophase to telophase, and how chromosomes are separated into two daughter cells.
Cyclins and CDKs
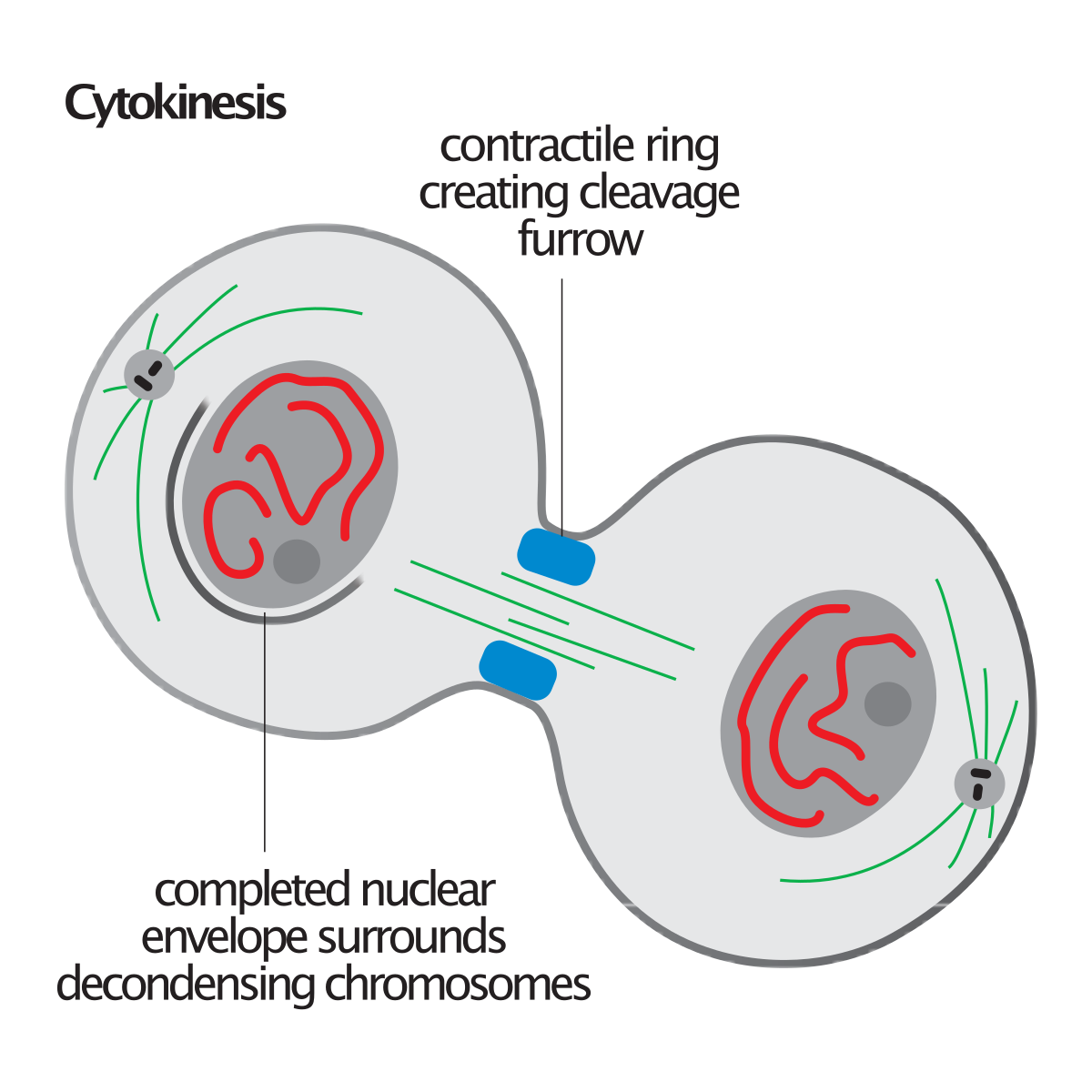 This image shows the process of cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm after mitosis, and the role of cyclins and CDKs in regulating the cell cycle.
This image shows the process of cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm after mitosis, and the role of cyclins and CDKs in regulating the cell cycle.
If you are searching about Cell Cycle Regulation: Cyclins and CDKs - PraxiLabs you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Cell Cycle Regulation: Cyclins and CDKs - PraxiLabs like What Is a Mitogen? (with picture), Cytokinesis: Definition, Steps, and Significance and also What Is a Mitogen? (with picture). Here it is:
Cell Cycle Regulation: Cyclins And CDKs - PraxiLabs
 blog.praxilabs.comcytokinesis mitosis cytoplasm kompas regulation tahap edurev cyclins sel chromosomes cdks neet
blog.praxilabs.comcytokinesis mitosis cytoplasm kompas regulation tahap edurev cyclins sel chromosomes cdks neet
Cytokinesis: The Process That Follows The Last Stage Of Mitosis. With
 www.pinterest.comcytokinesis mitosis cell division edupic cells stage two membrane cycle chromosomes telophase last simple process dna complete eukaryotic daughter different
www.pinterest.comcytokinesis mitosis cell division edupic cells stage two membrane cycle chromosomes telophase last simple process dna complete eukaryotic daughter different
What Is A Mitogen? (with Picture)
 www.wisegeek.comcytokinesis mitosis wisegeek facts mitogen chromatid cells process chromatids stratum occurs cell germinativum animal following replicate undergo part plant skin
www.wisegeek.comcytokinesis mitosis wisegeek facts mitogen chromatid cells process chromatids stratum occurs cell germinativum animal following replicate undergo part plant skin
Cytokinesis: Definition, Steps, And Significance
 www.scienceabc.comcytokinesis cell
www.scienceabc.comcytokinesis cell
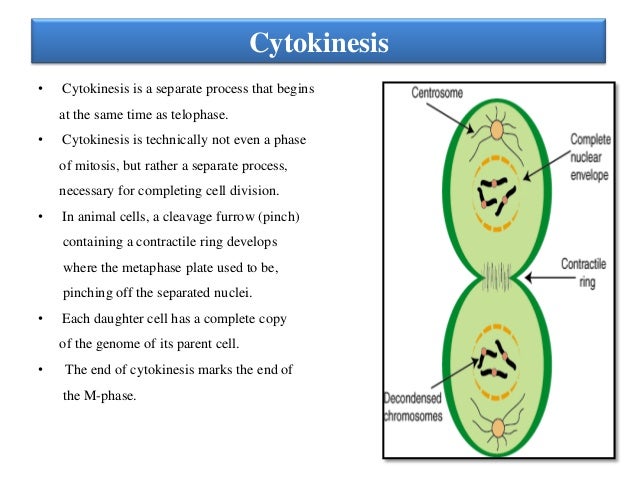
The Cell Cycle
 www.slideshare.netcytokinesis
www.slideshare.netcytokinesis
Cytokinesis: definition, steps, and significance. Cytokinesis mitosis cytoplasm kompas regulation tahap edurev cyclins sel chromosomes cdks neet. What is a mitogen? (with picture)